Office Syndrome
Group of Occupational Diseases Office Syndrome is a common disease of the work. The disease is usually caused by the use of any posture repetition or prolong using the computer. Diseases in this group include migraines, chronic headaches, neck pain, back pain, arm pain, wrist pain, hearing loss and nerve impingement eg. carpal tunnel syndrome, etc
Incidence
Experience pain mostly found in people of working age 60-70%, aged between 16-35 years. Of workers aged 55 years and over, often with a headache because they are responsible for important decisions.
Causes of Pain
Risk factor
Personal factors : age, body obesity, personal habits are a serious personal health concerns.
Environmental factors : workplace abuse, in a confined space, too work hard, accident.
Psychological factors : Stress at work, Perfectionism, boring in the job.


Perpetuating factor
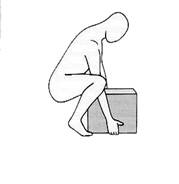
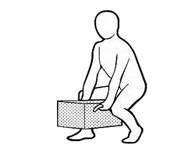
- Stay in the wrong position and repeat for a long time such as standing, sitting, leaning back, neck, round shoulder, forward posture, lifting incorrectly, high heel height, bed too soft.
- Type of work: labor-intensive task, vibrates machine, new work that never done before.
- Obesity: abdominal muscle weakness.
- Other health conditions: anemia, low thyroid, malnutrition, infections, depression
- Using too much works in the same position and repeat for long time.
- Accident: fell sharply.

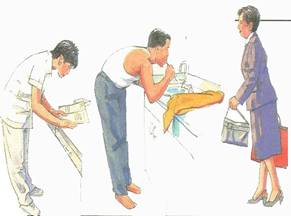
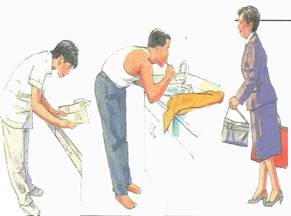
How to fix the pain
- Relaxation.
- The use of pain medication.
- Physiotherapy.
- Acupuncture to relieve muscle pain.
- Back brace.
- Exercise.
- Correction factors cause and prevent a recurrence.
Correct the two main causes
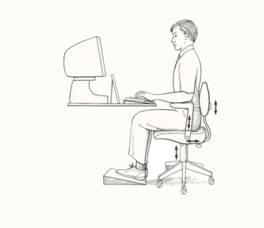
1. Working conditions : Conditions and hygienic working for a computer desk chair, correct ergonomic.
2. Body conditions : a structured body to fit the job, Organizing structure, Training structural balance, Increase physical strength through aerobic exercise.
If not better, with more latent factors.
- Excessive workload and overload.
- Stress (work colleagues. Personal).
Prevention of Pain
- Avoid risk factors include overworked prolonged stress, smoking, drinking, obesity.
- Maintain proper posture by posture biomechanics.
- All of the correct methods of lifting.
- Avoid places where the risk of harm to workers.
- Use equipment that fits properly and placing in operation.
- Muscle strength training regularly.
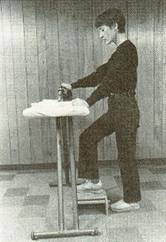
Care in a standing position
- Avoid standing in the wrong position.
- Carbon viscera every effort flexed posture.
- Standing on a base that is wide enough.
- Distribute the weight of each leg, alternating frequently, but not the weight on the hips.
- Place the legs on the little stool around.
- Try slightly flexed knee while standing long time.
- Wear the right shoes, The toes are not too narrow, Heel is not too high.
- Try to move around or change position frequently.
- Stand back cover flap and dropped back periodically.
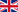
Care in a sitting position
- Straight back
- Fit Rigid backrest angle 90-100 °.
- Abstain from 90 ° elbow and arm.
- Keep natural keep of lumbar lordosis.
- Bend the hips perpendicular to the latter.
- Hips are level with the knee or above the knee.
- Vice Chair of the thighs fit & separate from popliteal knee~ 2 fingers.
- Foot pad fits the floor.
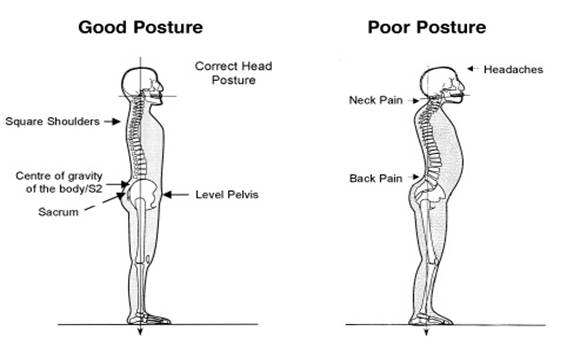
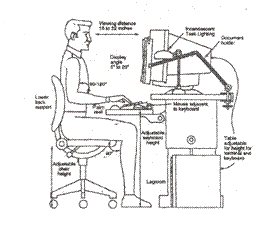
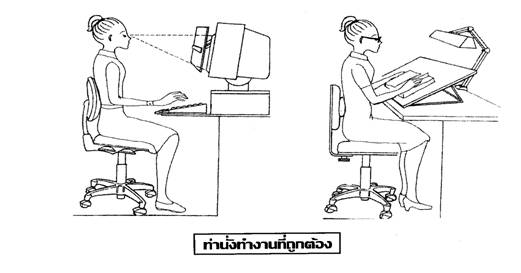
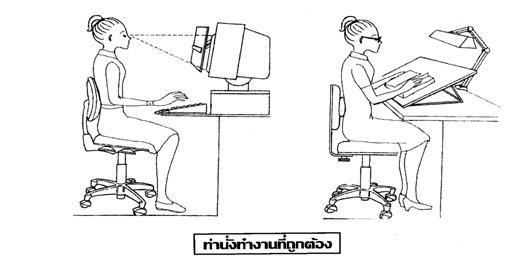
Correct posture while working
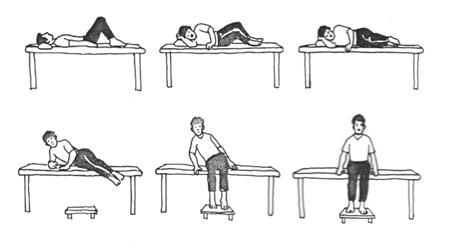
Prone to help loosen muscles in the lower back.
Sitting on the couch at right.
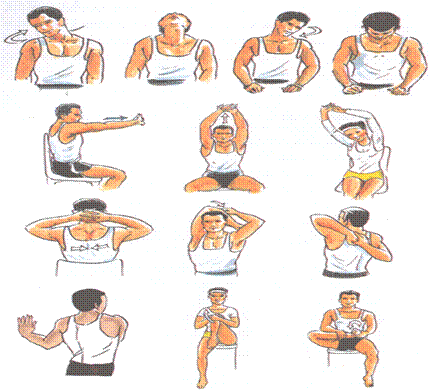
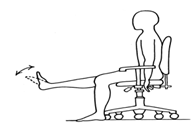
Workplace exercise.
Reference
1. Best Practice & Research Clinical Rheumatology Vol.22, No.4, pp. 677-691, 2008.
2. Musculoskeletal disorders and the workplace : low back and upper extremities/ Panel on Musculoskeletal Disorders and the Workplace, Commission on Behavioral and Social Sciences and Education, National Reseach Council and Institute of Medicine.
3. Low Back Syndromes : Integrated Clinical Management, Craig E. Morris 2006.
Edited by : Dr. Supannee Amnuaypornsathit, Physiatrist.